TLDR
Speed controllers (ESCs) regulate the speed and direction of electric motors. Whether you’re using them in drones, industrial machines, or electric vehicles, ESCs are essential for precise control. This article covers ESC types, how they work, installation tips, and how to choose the right one for your needs. Soltree offers a range of reliable ESCs that provide superior performance across multiple industries.
What is a Speed Controller?
A Speed Controller (also called an Electronic Speed Controller, or ESC) is an electronic device used to regulate the speed, direction, and braking of electric motors. ESCs are integral to a variety of applications, from drones and RC vehicles to industrial machinery and electric vehicles.
Types of Speed Controllers:
-
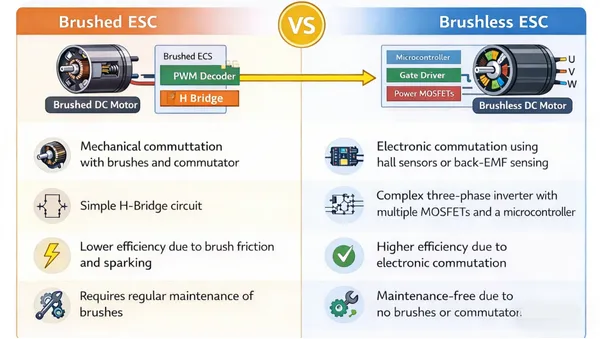
Brushed ESC: For brushed DC motors, simple and cost-effective.
-
Brushless ESC: For brushless DC motors (BLDC), more efficient, with a longer lifespan. Soltree‘s brushless ESCs are ideal for high-performance applications.
-
Linear ESC: Controls motor speed by dissipating excess energy, often used in noise-sensitive environments.
-
Switching ESC: Uses high-frequency Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) for high efficiency and low heat generation.
-
Pneumatic/Hydraulic Speed Controllers: Used in industrial systems to control actuator speed by regulating fluid flow.
Why are Speed Controllers Important?
-
Infinitely Variable Speed Control: Adjusts motor speed across a wide range.
-
Motor Protection: Prevents damage due to overload, overheating, and voltage fluctuations.
-
Precision Control: Essential for high-precision systems in automation and robotics, including Soltree‘s customized ESCs for industrial automation.
How Does a Speed Controller Work?
Basic Working Principle:
An ESC receives control signals, usually in the form of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) pulses, from a controller (e.g., a remote, PLC, or flight controller). The ESC adjusts the motor’s power supply by either converting DC power into a three-phase AC output (for brushless motors) or adjusting DC voltage (for brushed motors) to control speed.
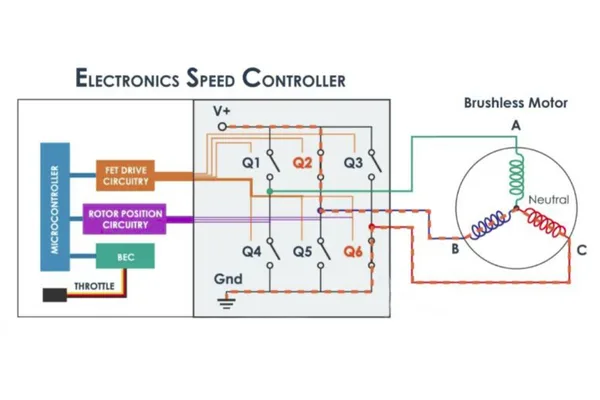
Key Components of an ESC:
-
Microcontroller (MCU): Processes control signals and manages motor position and speed.
-
MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors): Control current flow to the motor windings.
-
Battery Eliminator Circuit (BEC): Provides low-voltage power to the receiver and servos, often featured in Soltree‘s ESCs to ensure stable operation.
-
Gate Driver: Amplifies the signal from the MCU to drive the MOSFETs at a high switching frequency.
Control Methods:
-
PWM Control: Adjusts the width of electrical pulses to regulate motor speed.
-
Frequency Control: Increases the switching frequency for improved motor response.
-
Back EMF Detection (Sensorless Control): Used in brushless motors to detect rotor position at high speeds.
-
Hall Effect Sensors (Sensored Control): Provides precise control, especially at low speeds.
How to Install and Set Up Your Speed Controller
Installation Steps:
-
Check Flow Direction: Most ESCs include directional arrows to ensure proper installation and prevent reverse flow.
-
Install Close to the Actuator: Place the ESC near the motor to reduce response delay and improve control accuracy.
-
Clean Tubing Before Installation: Ensure the tubing is free from dust or debris to avoid clogs.
-
Secure Properly: Tighten the ESC without over-tightening to avoid leaks or damage.
-
Adjust Flow Gradually: Start with a low setting and gradually increase while observing system performance.
Environmental and Safety Considerations:
-
Avoid Extreme Temperatures and Humidity: Install in a dry, cool environment.
-
Ensure Proper Ventilation: Adequate airflow prevents overheating.
-
Follow Electrical Safety Standards: Always disconnect power before installation.
How to Choose the Right Speed Controller
Match Motor Type:
-
Brushed Motors: Use Brushed ESCs.
-
Brushless Motors: Use Brushless ESCs (Sensorless or Sensored).
-
AC Motors: Use Variable Frequency Drives (VFD).
-
Stepper/Servo Motors: Use Specialized Drivers.
Key Parameters to Consider:
-
Current Rating: Select an ESC with a current rating 10-30% higher than the motor’s maximum current.
-
Voltage Range: Ensure the ESC matches your battery’s voltage (e.g., 2S-6S LiPo).
-
Size and Weight: Choose an ESC that fits your system’s size and weight requirements.
-
Protocol Compatibility: Ensure the ESC supports the necessary protocols (e.g., PWM, DShot, CAN).
-
Firmware Support: Look for ESCs with updatable firmware for flexibility.
Application Recommendations:
-
Drones: Lightweight ESCs with high refresh rates and DShot support for faster responsiveness.
-
Industrial Automation: ESCs with high reliability and good thermal management, such as Soltree’s ESCs for industrial environments.
-
Electric Vehicles: ESCs supporting regenerative braking and energy management.
-
Home Appliances: Quiet, energy-efficient ESCs for easy integration.
Communication Between ESCs and Motors
Common Protocols:
-
PWM: Stable, traditional analog signal.
-
DShot: Digital signal with high resistance to interference and supports bidirectional communication (telemetry data).
-
OneShot/Multishot: High-speed protocols, ideal for racing drones.
-
CAN/Cyphal: Suitable for distributed systems with multi-device communication.
System Integration Tips:
-
Use 4-in-1 ESCs: Saves space and simplifies wiring, especially for quadcopters.
-
Integrate with Flight Controllers and Sensors: Enables smarter control systems.
-
Support for Hot-Swapping: Makes maintenance and upgrades easier.
FAQ
-
What is the main function of a Speed Controller?
It controls motor speed, direction, and braking, ensuring the motor operates safely and efficiently in various applications. -
How do I choose the right ESC?
Select an ESC based on motor type, voltage, current rating, and application requirements. Ensure it supports the necessary protocols for optimal performance. -
Can one ESC be used for all motor types?
No. Each motor type (e.g., brushed, brushless, AC, DC) requires a specific ESC designed to handle its unique requirements. -
Why is the installation environment important?
Dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures can damage ESCs. Install them in clean, dry areas with good ventilation to avoid overheating and failure. -
What should I do if my ESC overheats?
Check for overload, ensure proper airflow, and consider adding heat sinks or cooling mechanisms to prevent thermal stress and prolong ESC life. -
How does a Speed Controller work?
An ESC receives control signals and adjusts the motor’s power supply, either converting DC to AC for brushless motors or adjusting DC voltage for brushed motors. -
What does a 4-in-1 ESC mean?
A 4-in-1 ESC integrates four ESCs into a single unit, simplifying wiring and saving space, commonly used in quadcopters and multi-motor applications. -
How to tell if your speed controller is bad?
Signs of a bad ESC include motor failure to start, erratic behavior, overheating, or abnormal noises. These can indicate issues with internal components or wiring. -
Can I put a speed controller on any motor?
No, a speed controller must match the motor type and specifications. Using an incompatible ESC can damage both the ESC and the motor.
Why Speed Controllers Are Essential in Modern Systems
Speed controllers are integral to modern motor-driven systems. They provide precise control over motor speed, direction, and braking, and protect the system from damage. From drones and electric vehicles to industrial machinery, ESCs ensure smooth operation and enhance efficiency across a wide range of applications. Soltree’s ESCs are designed to meet the needs of various industries, offering reliable and high-performance solutions.
Conclusion
This article provides a comprehensive look at Speed Controllers (ESCs), including their types, working principles, installation tips, and how to select the right one for your motor and application. ESCs are essential components for precise motor control, and understanding their functions and selection criteria can help improve the performance and longevity of your system. Soltree offers top-quality ESC solutions tailored to meet specific application needs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.